How Does a Solar Power System Work? A Simple Guide for Indian Homes
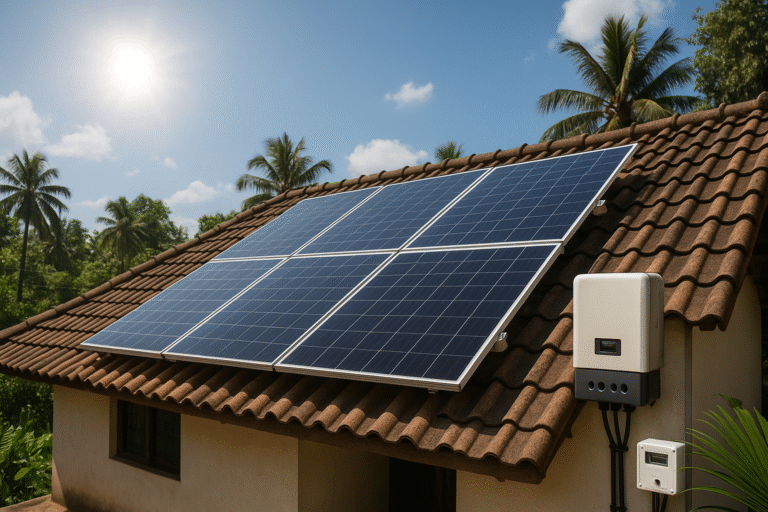
Solar energy has become one of the most popular and practical solutions for Indian households looking to reduce electricity bills and embrace a sustainable lifestyle. Yet, many homeowners still ask the basic but important question: how does a solar power system actually work?
In this beginner-friendly guide, we explain how solar power systems function, what components are involved, and how you can benefit from installing one in your home.
Understanding the Basics
A solar power system converts sunlight into usable electricity for your home. It does this using a combination of technologies that work together in a seamless flow of energy from the sun to your switches
Step-by-Step: How Solar Power Reaches Your Home
1. Sunlight Hits the Solar Panels
Solar panels are installed on rooftops or open spaces that receive maximum sunlight. These panels contain photovoltaic (PV) cells that absorb sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity.
2. Inverter Converts DC to AC
Since most Indian homes use alternating current (AC) electricity to run appliances, the DC power from the panels is passed through a solar inverter. This device converts DC to AC, making the electricity usable inside your home.
3. Power Your Home
The AC electricity is now fed into your home’s electrical system. It powers your lights, fans, air conditioners, washing machines, and more — just like electricity from the grid.
4. Net Meter Records Power Usage
In a grid-tied solar system, a net meter tracks how much electricity you generate, how much you consume, and how much excess power (if any) is sent back to the grid. If your system generates more power than you use, you receive credits that reduce your future bills.
Key Components of a Solar System
- Solar Panels: These capture sunlight and produce electricity.
- Inverter: Converts DC electricity into usable AC power.
- Mounting Structure: Holds panels in place, usually tilted for maximum sunlight.
- Wiring and Protection Devices: Ensures safe and efficient energy transfer.
- Battery (optional): Stores excess electricity for use during power cuts or at night.
Types of Solar Power Systems for Homes
- Grid-Tied System: Connected to the local electricity grid. Excess power is sent to the grid.
- Off-Grid System: Completely independent, using batteries for storage. Ideal for remote areas.
- Hybrid System: Combines solar power, batteries, and the grid for maximum flexibility.
Why Go Solar?
- Save on Electricity Bills: Cut down your monthly expenses significantly.
- Low Maintenance: Most systems require only occasional cleaning and annual checkups.
- Government Subsidies: Up to 40% subsidy available under national solar schemes.
- Green and Clean: Reduce your carbon footprint and contribute to a cleaner planet.
Final Thoughts
Installing a solar power system in your home is not just a trend it’s a practical step toward long-term savings and energy independence. Understanding how the system works can help you make smarter choices and get the most out of your investment.
Thinking about going solar? Contact a trusted installer to assess your roof, design your system, and start your journey toward a sustainable energy future.



